Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication to Strengthen Defense Against Data Breaches
In today's digital world, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. With the exponential growth of online transactions, the proliferation of connected devices, and the rise of sophisticated cyber threats, safeguarding sensitive information has become an equally serious concern for individuals, businesses, and governments.
One of the most pressing challenges in cybersecurity is the persistent threat of data breaches. These breaches can have devastating consequences, ranging from financial losses and reputational damage to regulatory penalties and legal ramifications.
According to the 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report by Verizon, over 80% of data breaches involve stolen or weak credentials, highlighting the critical role of authentication mechanisms in preventing unauthorised access.
How to Secure Data Breaches?
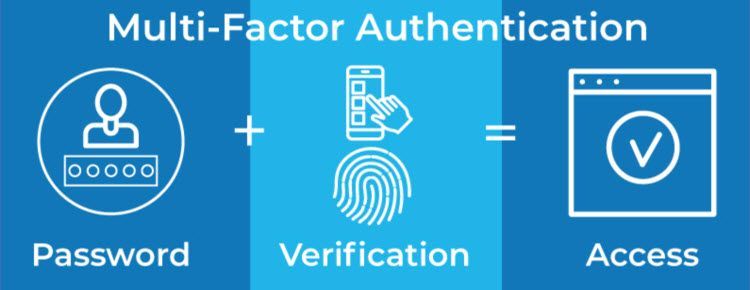
One of the most secure ways to mitigate data breaches is to implement multi-factor authentication (MFA), a powerful defence mechanism designed to mitigate the risk of unauthorised access by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before granting access to a system or application.
Unlike traditional password-based authentication, which relies solely on something a user knows (i.e., a password), MFA incorporates additional factors such as something a user has (e.g., a mobile device or security token) and something a user is (e.g., biometric data like fingerprint or facial recognition).
Understanding Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Before implementing Multi-Factor Authentication, it is imperative to understand the concept of MFA.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA), also known as two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-step verification, is a security mechanism that requires users to provide two or more authentication factors to verify their identity before gaining access to a system, application, or online account.
By adding an extra layer of security beyond passwords, MFA helps to thwart unauthorised access attempts, even if a password is compromised.
Types of Authentication Factors
It can be categorised into three main types based on the types of factors used and all of them are explained in the below sections.
Knowledge Factors
These include passwords, PINs, or answers to security questions. While commonly used, knowledge factors alone are vulnerable to phishing attacks, brute-force attacks, and password theft.
Possession Factors
These factors include physical devices such as smartphones, security tokens, or smart cards. Possession factors add an extra layer of security by requiring users to possess a specific device or token to authenticate physically.
Inherence Factors
They include biometric data such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans. Biometric authentication offers a high level of security and convenience, as biometric traits are unique to each individual.
Key Takeaway:
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a powerful tool for defending against data breaches by adding an extra layer of security beyond passwords. Understanding the best practices, and challenges is crucial for the effective implementation and protection of digital assets.

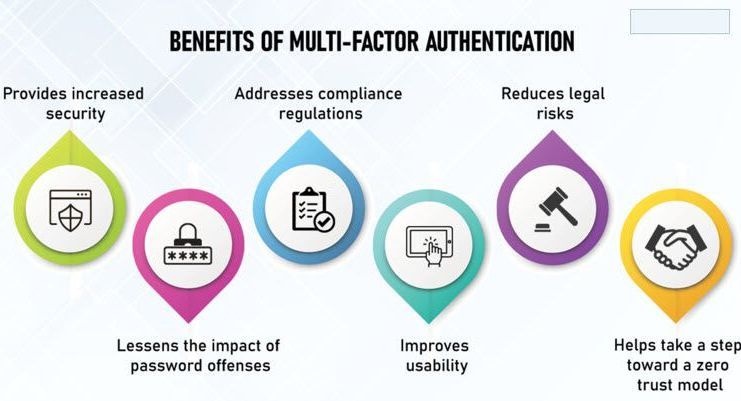
Benefits of Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) offers a wide range of benefits for individuals and organisations seeking to enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect sensitive data.
By requiring multiple forms of verification, MFA adds an extra layer of security that significantly reduces the risk of unauthorised access and data breaches.
Below are some key benefits of implementing multi-factor authentication:
Enhanced Security Layer
MFA provides a higher level of security compared to traditional password-based authentication methods. By requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification, such as a password and a unique code sent to their mobile device, MFA helps mitigate the risk of unauthorised access, even if one factor is compromised.
With the increasing rate of phishing attacks, brute-force attacks, and credential stuffing, it serves as an effective tool against them.
Protection Against Intellectual and Credential Theft
Password theft is a common tactic used by cybercriminals to gain unauthorised access to accounts and sensitive information. By implementing it, organisations can significantly reduce the risk of credential theft, as attackers would need more than just a password to access an account.
Compliance with Updated Regulatory Requirements
Many regulatory frameworks and industry standards, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), require organisations to implement multi-factor authentication as part of their security measures.
By implementing MFA, organisations can ensure compliance with these regulations and standards, reducing the risk of penalties and fines.
Enhanced User Convenience and Experience
Despite adding an extra layer of security, it can also enhance user convenience and experience, particularly when using modern authentication methods such as biometrics or mobile authentication apps.
With features such as biometric authentication like fingerprint or facial recognition and push notifications to mobile devices, it provides a seamless and user-friendly authentication experience.
Best Practices in Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires careful planning and consideration to ensure its effectiveness and seamless integration into existing systems and workflows. Below are some best practices for implementing MFA.
Choosing the Right MFA Solution
It is critical to evaluate different MFA solutions based on factors such as security features, compatibility with existing systems, scalability, and ease of use.
For example, a corporation should opt for a cloud-based MFA solution that integrates seamlessly with its existing identity management platform and offers a wide range of authentication methods, including SMS codes, mobile app authentication, and biometric verification.
Assessing Risk and Selecting Appropriate Factors
It is recommended that a risk assessment be conducted to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities that MFA can help mitigate. Then, select authentication factors based on the level of risk associated with different access points and user roles.
For instance, a Bank with high-risk transactions implementing MFA for online banking transactions requires customers to provide both a password and a one-time passcode sent to their registered mobile device.
Educating Users on MFA Usage and Benefits
Once you include MFA Protocol in your cybersecurity, you should provide comprehensive training and educational resources to users on how to enrol in and use MFA.
Emphasise the importance of MFA in enhancing security and protecting sensitive information.
For example, corporate sectors conduct regular security awareness training sessions for employees, highlighting the benefits of MFA and demonstrating how to set up and use different authentication methods, such as mobile app authentication and hardware tokens.
Seamless Integration with Existing Systems and Applications
Compatibility of MFA with your current system and application is very important. You have to ensure seamless integration of MFA with existing systems, applications, and workflows to minimise disruption and maximise user adoption.
For example, a Healthcare organisation looking to integrate MFA into its electronic health records (EHR) system, allowing healthcare providers to securely access patient data, would use a combination of passwords and biometric authentication.
This way, multi-factor authentication is seamlessly integrated into the existing login process, ensuring minimal impact on workflow efficiency.
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
More than implementing MFA will be required; implementing mechanisms for monitoring MFA usage, detecting anomalies, and responding to security incidents in real-time is crucial.
Regularly reviewing MFA policies and configurations is advised to identify areas for improvement and optimization.
For instance, some military sectors should employ a security operations center (SOC) to monitor MFA authentication logs and analyse user authentication patterns.
Any suspicious activities or unauthorised access attempts are promptly investigated and remediated.
Challenges and Considerations of Implementing MFA
While implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) offers numerous benefits, there are also several challenges and considerations that organisations must address to ensure its successful deployment and adoption.
User Adoption and Resistance
Being an extra security layer, some users may perceive MFA as cumbersome or inconvenient, leading to resistance and reluctance to adopt the technology, and thus, organisations should invest in user education and training.
Potential Technical Issues
Compatibility issues with legacy systems or applications may arise during the implementation of MFA, requiring careful planning and coordination with IT teams.
Maintenance and Scalability
Managing MFA solutions and maintaining authentication factors like tokens and biometric data for a large user base can be challenging and resource-intensive. It needs to develop robust processes for provisioning, de-provisioning, and updating authentication factors.
Balancing Security and User Experience
Striking the right balance between security and user experience is essential to encourage adoption and minimise friction. It is important to evaluate authentication methods that maintain the user experience.
Conclusion
In an era where data breaches are rampant and cyber threats continue to evolve, implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) is crucial. By implementing MFA and adhering to best practices, organisations and individuals can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture, fortifying defences against unauthorised access and data breaches.
As technology advances, staying ahead of cyber threats requires a proactive approach. MFA serves as a cornerstone in this ongoing battle to safeguard digital assets and preserve trust in the digital ecosystem.
Be informed. Stay updated.
Stay ahead with the
HermesHerald newsletter!
Immerse yourself in exclusive insights and crucial updates. Ensure you're always in the know!
Contact Us
Thank you for signing up to HermesHerald! We're excited to keep you updated with the latest insights and information. Stay tuned! 🌟
Please try again later.
Contact Us
Thank you for signing up to HermesHerald! We're excited to keep you updated with the latest insights and information. Stay tuned! 🌟
Please try again later.
Contact Us
Thank you for signing up to HermesHerald! We're excited to keep you updated with the latest insights and information. Stay tuned! 🌟
Please try again later.
With over 40 years combined experience, we conduct professional investigation and intelligence services for local and international clients in the public, private, and law enforcement sectors.
Website Privacy Policy & GDPR | Operational Policy
BROWSE WEBSITE
CONTACT INFO
Phone:
1800 889 713
Email: help@cyberlutions.com.au
Location:
Suite 88, 30 Denison St, Bondi Junction NSW 2022
Location:
Unit 4, 95 Main Rd, George Town TAS 7253
BUSINESS HOURS
- Mon - Fri
- -
- Sat - Sun
- Closed
With over 40 years combined experience, we conduct professional investigation and intelligence services for local and international clients in the public, private, and law enforcement sectors.
BROWSE WEBSITE
CONTACT INFO
Phone: 1800 889 713
Email: help@cyberlutions.com.au
Location: Suite 88, 30 Denison St, Bondi Junction NSW 2022
Location: Unit 4, 95 Main Rd, George Town TAS 7253
BUSINESS HOURS
- Mon - Fri
- -
- Sat - Sun
- Closed
Copyright CYBERLUTIONS, All Rights Reserved
Content, including images, displayed on this website is protected by copyright laws. Downloading, republication, retransmission or reproduction of content on this website is strictly prohibited. Website Privacy Policy & GDPR | Operational Policy | Cookie Policy








