Securing Sensitive Information from Breaches Using Best Practices in Data Encryption

Introduction
In an era of increasing data breaches and cyber threats, protecting sensitive information is extremely important. As more of our lives shift into the digital realm, from financial transactions to personal communications, the need to safeguard our data from prying eyes has never been more pressing.
That is where data encryption emerges as a fundamental tool in the arsenal of cybersecurity measures.
What is Data Encryption?
Data encryption converts plaintext information into ciphertext, making it unreadable to everyone without the appropriate decryption key.
It is a crucial safeguard against unauthorised access, ensuring that even if data falls into the wrong hands, it remains indecipherable and thus unusable.
The risks associated with data breaches are beyond the financial losses and reputational damage you may incur; in fact, the exposure of sensitive information can have far-reaching consequences for individuals, such as privacy infringements.

Exploring Encryption Techniques
When protecting your data, understanding the different encryption techniques available is crucial.
Encryption is like the lock on the door of your digital world, keeping your sensitive information safe from prying eyes.
Let's explore three primary encryption techniques: symmetric, asymmetric, and hybrid.
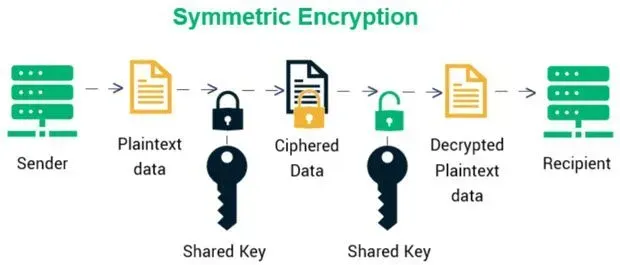
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption is like having a single key to lock and unlock your door. It uses the same key for both encryption and decryption.
It means that whoever has the key can encrypt and decrypt the data. The key here is to keep this key safe and secure because your data could be compromised if it falls into the wrong hands.
Pros
- Fast and efficient for encrypting large amounts of data.
- Simple and easy to implement.
Cons
- Key distribution can be challenging, especially if you must securely share the key with multiple parties.
- If the key is compromised, all encrypted data becomes vulnerable.
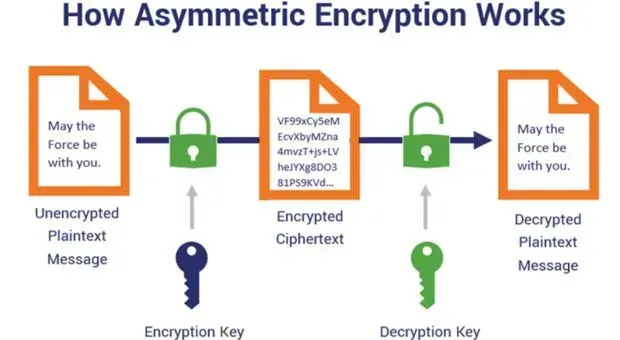
Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, is like having two keys. One to lock the door and another to unlock it.
Unlike symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption uses a pair of keys called public and private keys.
The public key is freely available to anyone and is used for encryption, while the private key is kept secret and is used for decryption.
Pros
- It offers a secure key exchange as you only share the public key.
- It allows you to sign documents, verifying their authenticity and integrity digitally.
Cons
- It is slower than symmetric encryption due to the complex mathematical operations involved.
- Requires more computational resources because of its complexity.
Hybrid Encryption
Hybrid encryption combines the strengths of both symmetric and asymmetric encryption. It addresses the challenge of key distribution in symmetric encryption by using asymmetric encryption to securely exchange a shared key, which is then used for symmetric encryption of the actual data
Pros
- Efficient key management of symmetric encryption for encrypting large amounts of data.
- By combining both encryption techniques, hybrid encryption provides robust protection against attacks.
Cons
- It requires careful integration of both symmetric and asymmetric encryption algorithms.
Crucial Implementation Tips
Now that we've explored the fundamental encryption techniques, it's time to discuss how to implement encryption effectively to safeguard your sensitive information.
Implementing encryption requires careful consideration of various factors, including selecting the right encryption algorithms and integrating encryption into your systems and applications.
Here are some implementation tips to guide you in securing your data effectively:
Selecting the Right Encryption Algorithms and Key Lengths
Choosing the appropriate encryption algorithms and key lengths is crucial for ensuring the security of your encrypted data. Consider the following factors when selecting encryption algorithms.
Strength and security
It is recommended that well-established encryption algorithms widely recognised for their security features be opted for, such as AES for symmetric encryption and RSA for asymmetric encryption.
Reasonable Key length
Longer key lengths typically provide stronger security but may require more computational resources. A suitable balance between security and performance is based on your needs and requirements.
Stay Up to Date
Stay updated on advancements in encryption technology and adopt new algorithms or key lengths as needed to mitigate emerging threats.
Integration of Encryption into Applications and Systems
Integrating encryption into your applications and systems requires careful planning and implementation to ensure seamless functionality and robust security.
Consider the following tips while integrating encryption into your system.
Identify sensitive data
Determine which data must be encrypted based on sensitivity and regulatory requirements.
Incorporate encryption into the design phase.
Integrate encryption into the design and architecture of your applications and systems from the outset to ensure comprehensive data protection.
Use encryption libraries and APIs
Leverage encryption libraries and APIs from reputable vendors to streamline the implementation process and ensure compatibility with industry standards.
Encryption in Transit vs. Encryption at Rest
Encryption can be applied to data in transit, like during communication between systems, and data at rest, like data stored on disk or in databases.
Consider the following tips for implementing encryption in transit and at rest:
Encryption in transit
Use secure communication protocols such as TLS (Transport Layer Security) to encrypt data transmitted over networks, preventing eavesdropping and tampering.
Encryption at rest
Encrypt data stored on disk or in databases using appropriate encryption mechanisms to protect against unauthorised access in case of a breach or physical theft.
Data Masking and Tokenization
In addition to encryption, consider employing data masking and tokenization techniques to enhance security and privacy.
Data masking
Replace sensitive data with masked or obfuscated values to protect confidentiality while preserving the format and structure of the data.
Key Takeaway
By understanding encryption techniques, adopting proper key management strategies, and staying compliant with regulations, individuals and organisations can enhance their data security posture and minimise the risk of unauthorised access to valuable data.
Duplicate Tokenization
Replace sensitive data with randomly generated tokens or surrogate values, which can be securely mapped back to the original data when needed.
Once encryption is implemented, it's essential to establish processes for continuous monitoring and updates to maintain the security of encrypted data.
Monitor encryption processes
Regularly monitor encryption processes and systems for anomalies or security incidents indicating potential vulnerabilities or breaches.
Update encryption systems
Stay proactive in applying patches, updates, and security fixes to encryption systems and software to address known vulnerabilities and mitigate emerging threats.
Conclusion
Data breaches continue to pose significant threats to individuals and organisations, highlighting the importance of implementing effective data encryption.
By leveraging encryption techniques such as symmetric, asymmetric, and hybrid encryption, coupled with sound key management strategies, businesses and individuals can bolster their defenses against cyber threats and safeguard sensitive information from unauthorised access.
Additionally, staying compliant with data protection regulations and continuously monitoring and updating encryption systems are vital to maintaining robust data security.









